According to the investment banking giant, the current stock market valuations are substantially correct.
With many stock markets reaching new highs, record issuances and a large number of deals in a row, fears that the markets may develop financial bubbles are also mounting. To help investors understand and avoid risks, Goldman Sachs has published a Global Strategy Paper which examines their characteristics and dangers, drawing the conclusion that current markets only present a few of the recurring features associated with bubbles. For example, there is no doubt that exceptionally-low interest rates can induce excessive risk-taking, but private sector finances are robust, thus reducing the chances of systemic risk in the absence of significant financial leverage, with the exception of government debts.
Neither Bubbles Nor Bear Market In Sight: According to Goldman Sachs, the initial phase of a recovery business cycle also suggests that the risk of impending bubbles, with their associated systemic risk, is relatively low. The investment company brings the example of Amazon.com Inc. and Apple Inc. stocks which, unlike in 2000, are not to be considered in bubble territory, since their respective fundamentals justify such high prices. The final verdict of the long and detailed analysis proposed by Goldman Sachs' "guide to bubbles" is that there are signs of complacency and high optimism in the market, but the key factors driving it and the cycle of economic recovery being just at the beginning seem to suggest that we are far from the explosion of a bubble. Moreover, as it can be evinced by the table below created by Goldman Sachs itself, bear market seems to be still in hibernation.
Absence Of Any Significant Leverage: Although Goldman admits the presence of pockets of overvaluations on the stock market, with some parts of it making adjustments consistent with the evolution of interest rates, there are no recurring features of bubbles, not even partial ones. Goldman particularly emphasizes the absence of any significant leverage - the only exception being the public sector, for it judges that the financial system stability risks are relatively low.
High Prices May Be Justified:Goldman's paper quotes Charles Mackay, who observed - already in 1841 - how human beings often "think" like a flock, but then do not necessarily behave as such when they finally menage to slowly grasp the meaning of things. Concerning the recent alarm triggered, by the Chinese regulator Guo Shuging, about bubbles swelling in the US and Europe, the analysis states that excessive prices of a single stock or applied to a limited part of the market do not necessarily indicate a systemic risk. Besides, not every swift price rise is related to a bubble, since it sometimes only signals a strong, genuine increase in value, justified by fundamentals.
Psychological Contagion: Psychology is a chief factor, as Robert Shiller pointed out in his book "Irrational Exuberance", published in 2000 and inspired by a famous quote from the then-Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan, who defined a bubble as the situation in which the news of rising prices provokes a contagion effect that spreads among investors, triggering a mechanism of envy for the success of others.
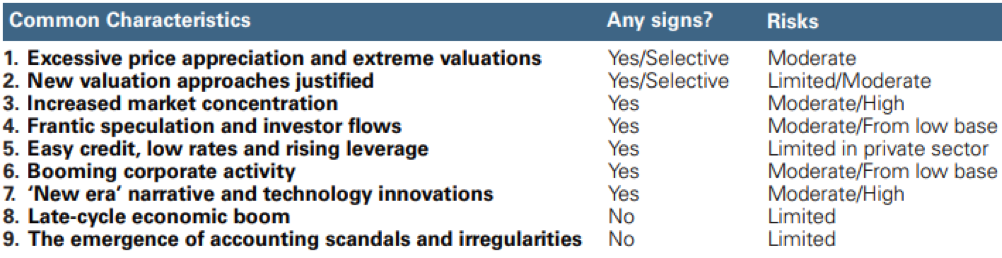
A Handful Of Recurring Ingredients: This sort of contagion has occurred several times over the centuries in human history - from the Dutch tulips of the 1600s to the bubbles of the South Seas and the Mississippi in Great Britain and France in the 1700s, not to mention the more recent Internet and subprime mortgage bubble, and passing through the "railway" bubble of last century in the United States. According to Goldman, the ultimate ingredients are few and never change: prices unanchored from reality, a justifying attitude, market concentration, widespread speculation, excess of leverage, the narration of being on the threshold of a new era and an end-of-cycle economic boom, all seasoned with scandals and behavior irregularities.

